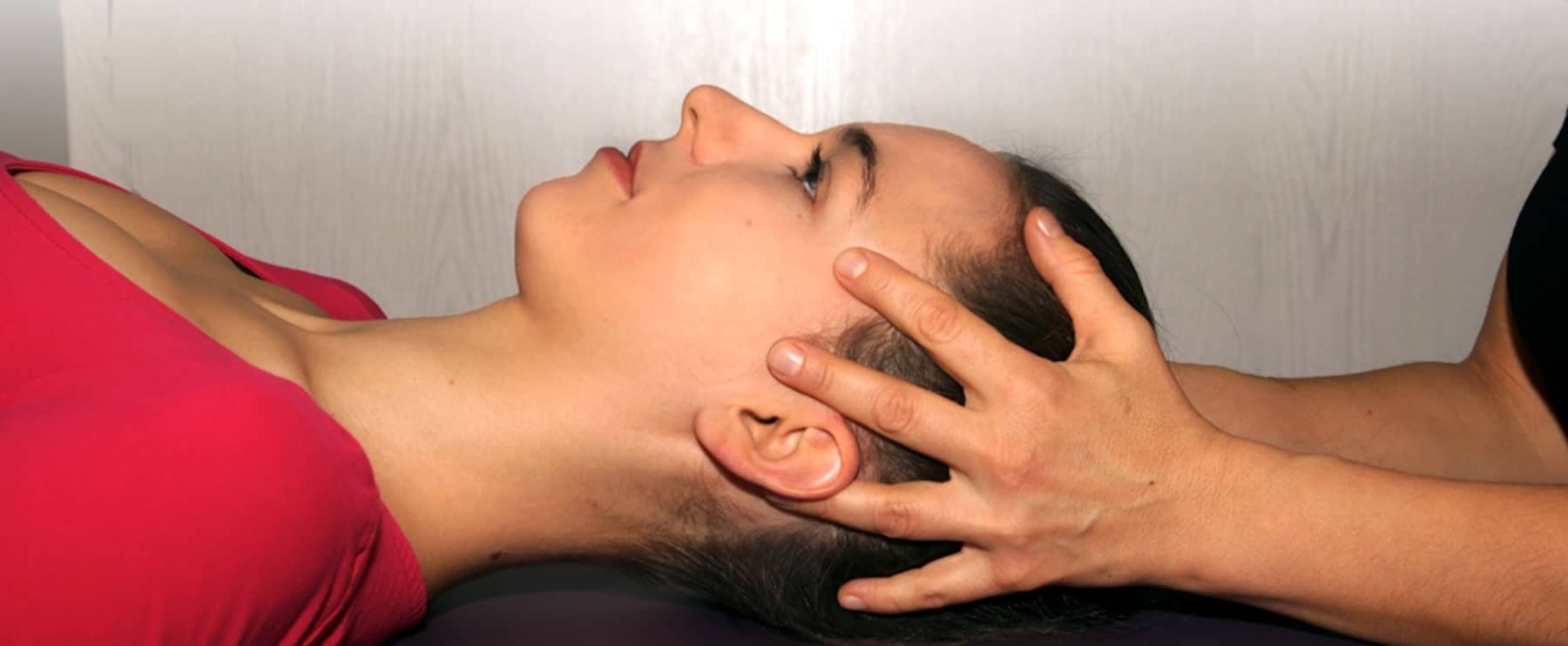
Osteopathy in our specialist practice for comprehensive orthodontics
The masticatory system controls the cranio-sacral system (CSS)
Every mother is familiar with her baby’s fontanel, a soft spot on the head. She also knows that the skull bones of babies and small children can still move slightly against each other. What is less well known is that this mobility must be maintained to a lesser extent throughout life in order to stay healthy. The American anatomist E. W. Retzlaff has now scientifically confirmed this. This necessary movement takes place roughly in rhythm with breathing and extends over the entire course of the meninges, i.e. from the head to the rump, and thus ensures that the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is nourished and kept healthy. There is a rhythmic expansion and contraction of the meninges, cranial bones, spinal column and sacrum complex. The intensive relationship between the masticatory system and the movable cranial bones leads to a direct dependence of the cranio-sacral system (CSS) on the function of the masticatory system. You could also say that the masticatory system controls the CSS.
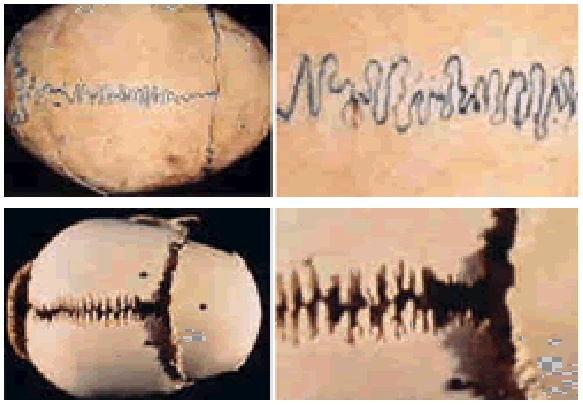
Disorders of the cranio-sacral system (CSS)
In almost all cases, disorders of the chewing muscles, the position of the lower jaw and the position of the teeth lead to CSS disorders. The holistic manual therapy treatment method of osteopathy can be carried out in three systems of the body as required: parietal (musculoskeletal system), visceral (internal organs) and cranio-sacral (dural system of the cranio-sacral complex). These three areas must function in harmony with each other. There is no doubt that the craniomandibular system plays a dominant role in the cranio-sacral system, which ultimately means a rhythmic expansion and contraction of the cranial bone, meninges, spine and sacrum.
Orthodontics & osteopathy for optimum long-term effect
In some cases, it is useful and in certain cases even necessary to accompany orthodontic treatment with osteopathic treatment. Through holistic osteopathic treatment or through targeted osteopathic correction of certain ascending lesions, e.g. starting from the feet or visceral area. The result is a long-term improvement in the organism’s self-regulatory abilities.
Symptoms of a disorder of the cranio-sacral system (CSS)
In many cases, it therefore makes sense to combine osteopathic treatment with comprehensive orthodontic treatment in order to achieve an optimal long-term effect. Typical symptoms are
- Pain in the course of the spine and sacrum
- Shoulder-arm pain
- Headache
- Migraine
- Dizziness
- Hormonal disorders
- Depression
- Chronic nosebleeds